最近在研究《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》,把一些自己的看法和代码实现写在这里,算是个记录吧,以免以后忘记。
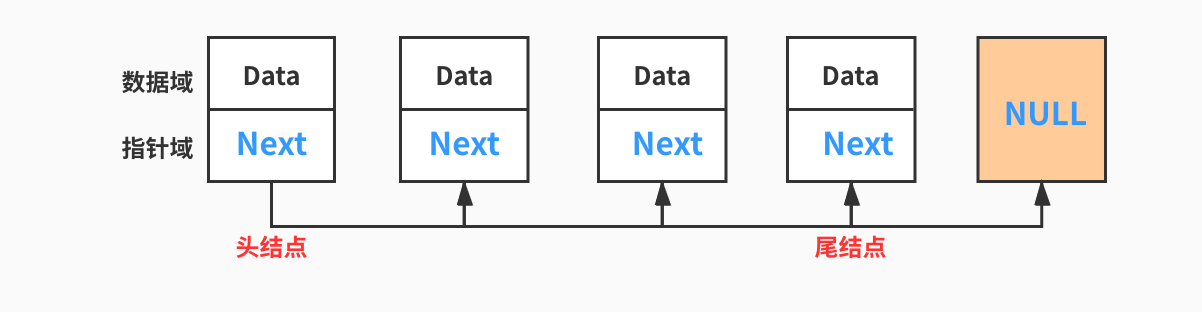
总所周知,数组中元素地址在内存中是连续分布的,而链表的元素在内存中的存储位置是随机的。其中比较简单的链表类型就是单向链表,这种类型的链表的每个节点只有一个链,且每个节点都连接下一个节点(除了最后一个节点:NULL用来标记链表的结束)。
为了用链表描述线性表,需要定义一个节点结构体,使用C++模板能够支持更多的类型
template <class T >struct chainNode {chainNode (){}chainNode (const T &data){this ->data=data;this ->next=nullptr ;chainNode (const T &data,chainNode*next){this ->data=data;this ->next=next;
我们需要定义一个类,用于管理链表操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 template <class T >class LinkedList {protected :int m_size;public :LinkedList ();LinkedList (const T&);LinkedList (const LinkedList<T>&);LinkedList (LinkedList<T>&&);virtual ~LinkedList ();void insert (int ,const T&) void append (const T&) void eraseByIndex (int ) void erase (const T&) void clearAll () bool empty () int size () int indexOf (const T&) T &get (int ) ;chainNode<T>*getFirstchainNode () ;chainNode<T>*getLastchainNode () ;void outputLinkedList ()
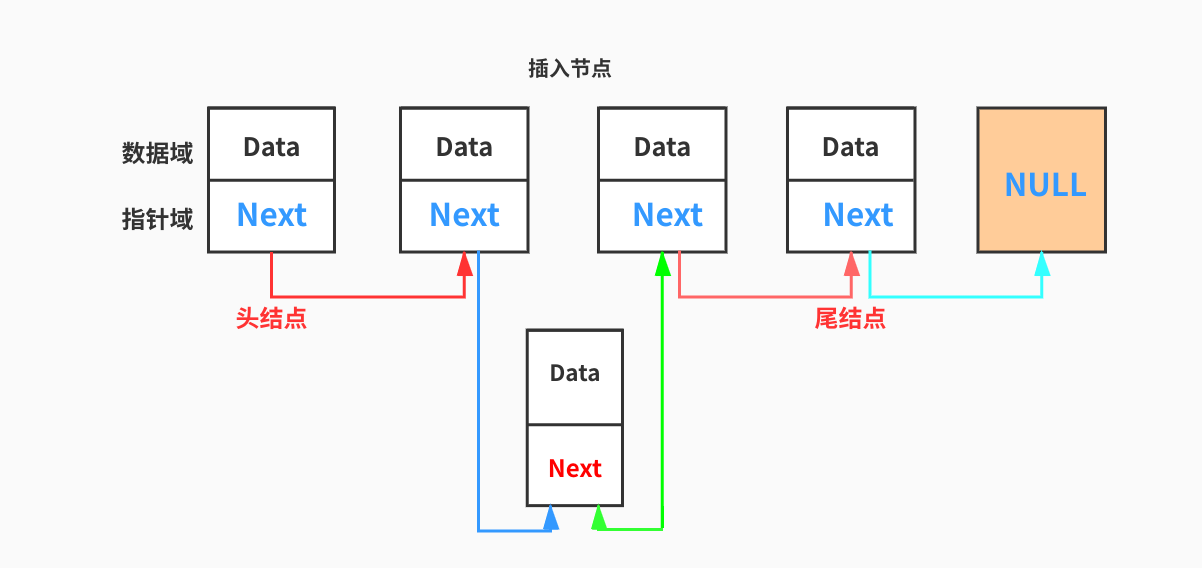
链表的插入其实很简单,首先需要找到索引index的节点,然后在该节点之后或者之前 插入新元素节点,那么?如何插入呢?其实就是通过 chainNode* next 指针将内存中的节点地址链接起来,chainNode* next 也只是一个变量标识符来标识内存中的地址罢了,因此我们可以通过替换next指针将需要插入的节点和已经存在的链表串起来,如下图所示
为了说明,我们先来一个最简单的例子,在链表尾处插入节点
代码如下
template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::append (const T&data){while (pNode->next){new chainNode<T>(data);this ->m_size++;
要在尾部插入节点,那么需要单向遍历整个链表,注意 while (pNode->next) 不能是 while (pNode) ,因为我们需要用尾节点添加一个新节点,同时更新链表大小
注意:可能有人会有疑惑:pNode=pNode->next 会让m_Header 指向下一个节点啊?其实 chainNode*pNode=m_Header; 只是将 m_Header 的地址值复制给pNode变量而已,虽然pNode会修改其地址值,但是它内存中的数据对象没有改变,改变的只是一个普通的指针变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::insert (int theIndex,const T&data){if (theIndex<0 ||theIndex>=m_size)return ; if (theIndex==0 && m_Header==nullptr ){new chainNode<T>(data);else {int index=0 ;while (pNode){if (index==theIndex){new chainNode<T>(data,pNode->next);
在介绍删除之前,我们需要输出链表节点内容方便调试,这段代码很简单,基本都是while(pNode)循环的套路
template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::outputLinkedList (){if (this ->m_Header==nullptr )return ;this ->m_Header;int index=0 ;while (pNode){"[" <<index<<"] => " <<pNode->data<<std::endl;
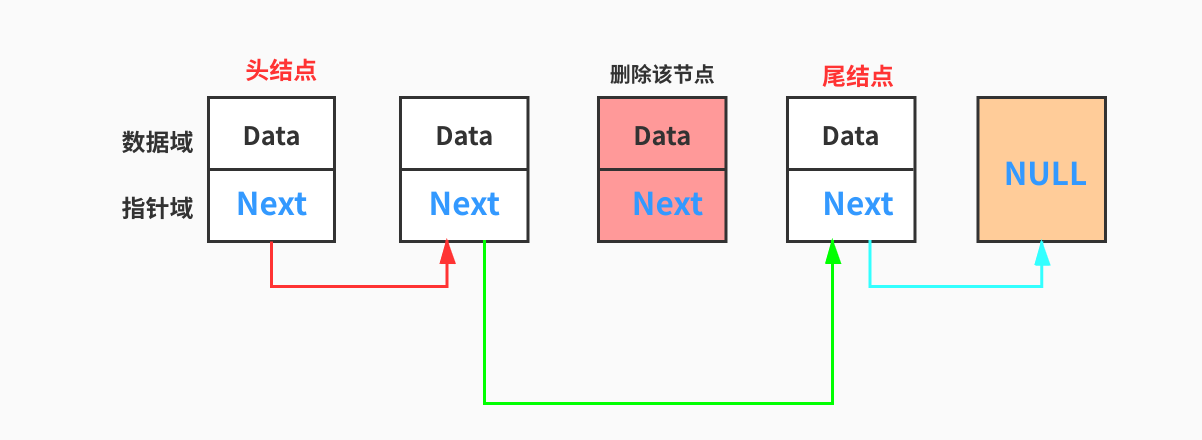
删除链表中的某个节点类似于插入节点,也是通过指针替换的手段,然后delete掉要删除的节点即可。不过有些地方需要注意。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::eraseByIndex (int theIndex){if (theIndex<0 || theIndex>=m_size)return ; nullptr ;if (theIndex==0 ){else {for (int i = 0 ; i < theIndex-1 ; i++){delete deletedNode;nullptr ;
其中要注意如果要删除索引为0的节点也就是头结点,那么只需要让头结点更新为原来的下一个节点,然后再delete要删除的节点,这种情况很特殊,因为单向链表头结点无前驱节点 。其他情况需要一个前驱节点(也就是当前节点的上一个节点)来衔接整个链表。
再来看下面的代码,删除链表中所有数据为data的节点,同时还处理的头结点的特殊情况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::erase (const T&data){while (pNode){if (pNode->data==data){if (pNode==m_Header){auto next=m_Header->next;delete m_Header;else {delete pNode;
事实上,当真正了解的单向链表的插入删除的本质时,其他的链表类型也能理解。
单向链表是最基础的一种链表类型,当然还有其他的一些变种:循环列表、双向链表、双向循环链表、甚至是树结构(层次结构 )也与链表密不可分。因此,必须要对链表十分熟悉!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 template <class T >bool LinkedList<T>::empty (){return this ->m_Header==nullptr &&this ->m_size<=0 ;template <class T >int LinkedList<T>::size (){return this ->m_size;template <class T >int LinkedList<T>::indexOf (const T&data){int index=0 ;while (pNode&&pNode->data!=data){if (pNode==nullptr )return -1 ;else return index; template <class T >get (int index){if (index<0 || index>=m_size)throw length_error ("the index is invalid!" );int count=0 ;while (pNode&&index!=(count++)){return pNode->data;template <class T >getFirstchainNode (){return m_Header;template <class T >getLastchainNode (){auto p=m_Header;while (p&&p->next){return p;
完整代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 #pragma once #include <iostream> using namespace std;template <class T >struct chainNode {chainNode (){}chainNode (const T &data){this ->data=data;this ->next=nullptr ;chainNode (const T &data,chainNode*next){this ->data=data;this ->next=next;template <class T >class LinkedList {protected :int m_size;public :LinkedList ();LinkedList (const T&);LinkedList (const LinkedList<T>&);LinkedList (LinkedList<T>&&);virtual ~LinkedList ();void insert (int ,const T&) void append (const T&) void eraseByIndex (int ) void erase (const T&) void clearAll () bool empty () int size () int indexOf (const T&) T &get (int ) ;chainNode<T>*getFirstchainNode () ;chainNode<T>*getLastchainNode () ;void outputLinkedList () template <class T >LinkedList (){nullptr ;0 ;template <class T >LinkedList (const T&data){new chainNode<T>(data);1 ;template <class T >LinkedList (const LinkedList<T>&ll){if (ll.m_Header==nullptr )throw runtime_error ("The source object can not nullptr!" );this ->m_size=ll.m_size;this ->m_Header=new chainNode<T>(ll.m_Header->data);this ->m_Header;while (pNodeSource){new chainNode<T>(pNodeSource->data);nullptr ;template <class T >LinkedList (LinkedList<T>&&ll){this ->m_size=ll.m_size;this ->m_Header=ll.m_Header;nullptr ;template <class T >LinkedList (){if (this ->m_Header){this ->clearAll ();template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::insert (int theIndex,const T&data){if (theIndex<0 ||theIndex>=m_size)return ; if (theIndex==0 &&m_Header==nullptr ){new chainNode<T>(data);else {int index=0 ;while (pNode){if (index==theIndex){new chainNode<T>(data,pNode->next);template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::append (const T&data){while (pNode->next){new chainNode<T>(data);this ->m_size++;template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::clearAll (){while (m_Header){delete m_Header;nullptr ;nullptr ;0 ;template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::eraseByIndex (int theIndex){if (theIndex<0 ||theIndex>=m_size)return ; nullptr ;if (theIndex==0 ){else {for (int i = 0 ; i < theIndex-1 ; i++){delete deletedNode;nullptr ;template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::erase (const T&data){while (pNode){if (pNode->data==data){if (pNode==m_Header){auto next=m_Header->next;delete m_Header;else {delete pNode;template <class T >bool LinkedList<T>::empty (){return this ->m_Header==nullptr &&this ->m_size<=0 ;template <class T >int LinkedList<T>::size (){return this ->m_size;template <class T >int LinkedList<T>::indexOf (const T&data){int index=0 ;while (pNode&&pNode->data!=data){if (pNode==nullptr )return -1 ;else return index; template <class T >get (int index){if (index<0 ||index>=m_size)throw length_error ("the index is invalid!" );int count=0 ;while (pNode&&index!=count++){return pNode->data;template <class T >getFirstchainNode (){return m_Header;template <class T >getLastchainNode (){auto p=m_Header;while (p&&p->next){return p;template <class T >void LinkedList<T>::outputLinkedList (){if (this ->m_Header==nullptr )return ;this ->m_Header;int index=0 ;while (pNode){"[" <<index<<"] => " <<pNode->data<<std::endl;
其实我们还可以利用上面的单向链表实现一个简单的有序链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #pragma once #include "LinkedList.h" template <class T ,class Compare =class SortedLinkedList :public LinkedList<T> {public : using LinkedList<T>::LinkedList;using LinkedList<T>::insert;SortedLinkedList (){}void insert (const T&) template <class T ,class Compare >void SortedLinkedList<T,Compare>::insert (const T&data){this ->m_Header;nullptr ;while (pNode&&Compare ()(pNode->data,data)){if (pNodePre==nullptr ){this ->m_Header=new chainNode<T>(data,pNode);else {new chainNode<T>(data,pNode);this ->m_size++;
链表元素在内存随机存储的,占用一定的内存空间,且查找速度要慢于顺序表,但在插入和删除方面要优于顺序表。如果有一种数据结构够将两者结合起来,那么就能够充分利用两者的优点,这种数据结构就是跳表和散列表。